Discover the Remarkable Persistence of Inca Farming Techniques Through the Ages
In the heart of the Andes, where the rugged mountains meet the fertile valleys, lies a story of agricultural innovation that has endured for centuries. The Inca Empire, renowned for its engineering marvels, is equally distinguished for its sophisticated agricultural techniques. Today, the tools and practices developed by the Inca people continue to influence farming in the region, providing a timeless testament to their ingenuity. In this exploration, we’ll journey through the history of Inca agricultural tools and discover how they’ve left an indelible mark on modern farming practices.
The Ingenious Inca Agricultural System
The Inca Empire, which thrived in the 15th and 16th centuries, was characterized by its remarkable organization and engineering feats. At the heart of this civilization was its agricultural system, which allowed it to sustain a vast population. The Incas terraced mountainsides, creating flat platforms for cultivation, and developed an intricate irrigation network to optimize water usage. These methods are still in use today.
The Qollqas: Ancient Granaries
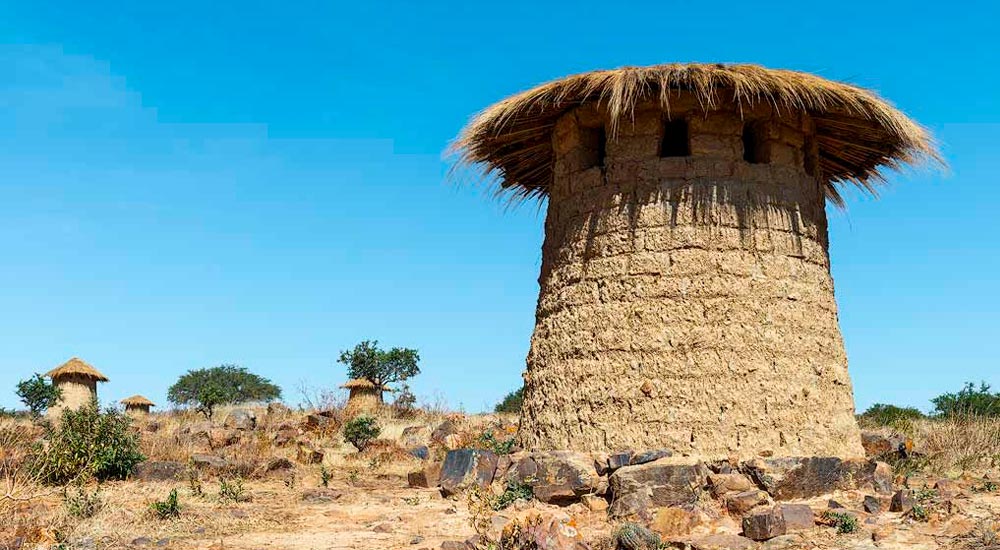

The Incas developed an ingenious storage system known as “qollqas.” These large, circular stone structures were built at various altitudes to take advantage of microclimates. The qollqas provided climate-controlled storage for crops like potatoes and maize, preserving them for times of scarcity. These structures served as early models for modern food storage facilities.
Tacllas: Farming Tools of the Past
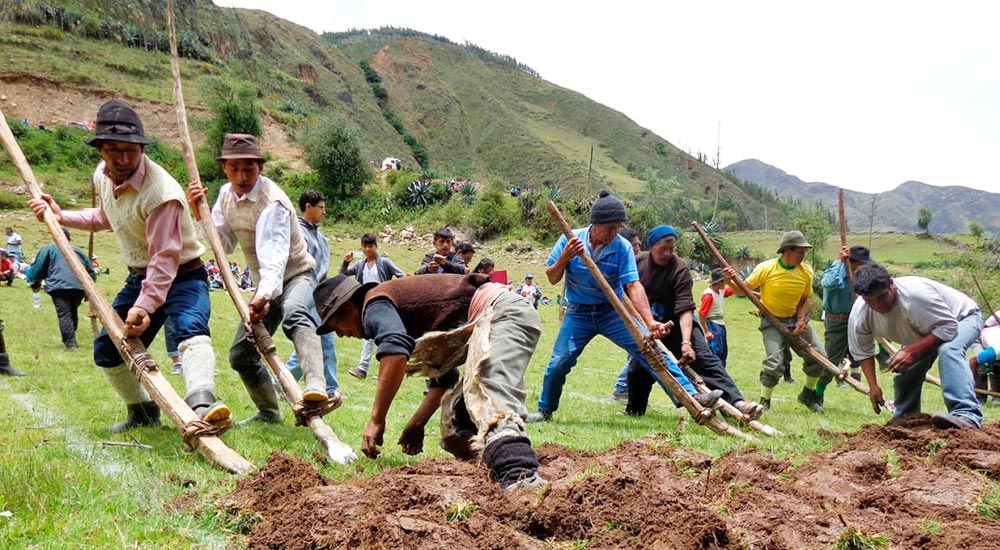

The Inca people crafted a variety of tools to facilitate their farming practices. The “taclla” is a prime example. This pointed stick was used for planting crops and digging irrigation channels. Its simplicity and effectiveness are qualities that continue to be valued by Andean farmers today.
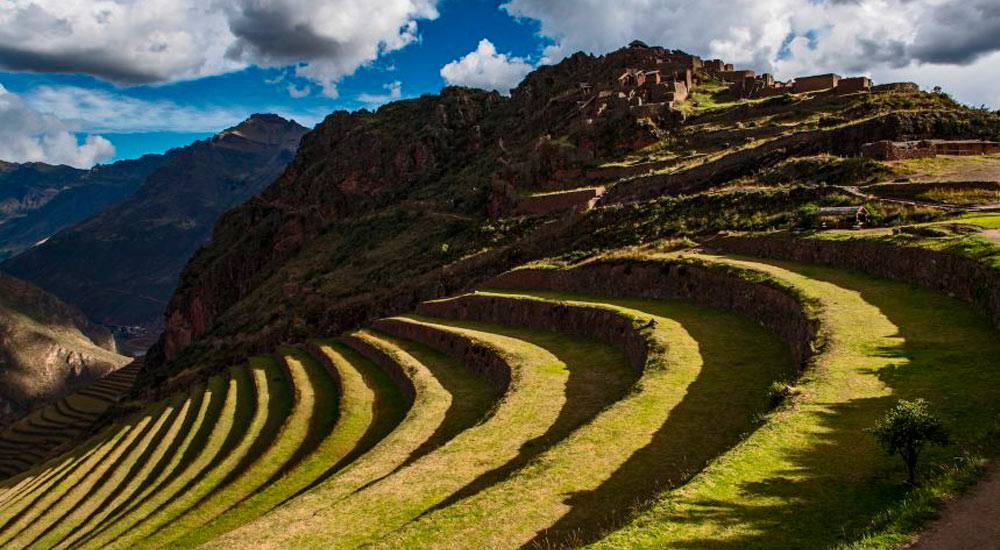
Andenes: The Terraces That Feed the Present
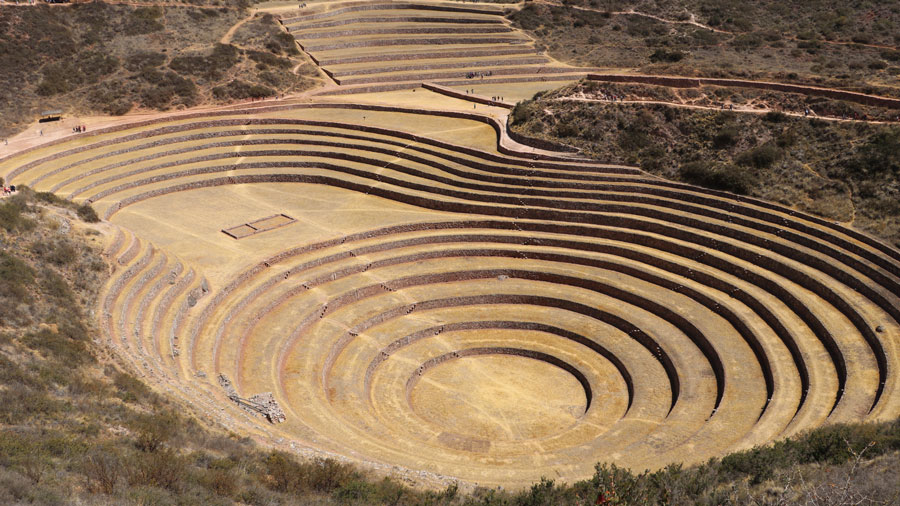

Perhaps the most iconic aspect of Inca agriculture is the “anden” or agricultural terrace. These stepped platforms, carved into steep slopes, provided arable land in high-altitude regions. The use of andenes is still prevalent in the Andes, where they allow farmers to cultivate crops like quinoa, amaranth, and various root vegetables.
The Chinampas of Lake Titicaca
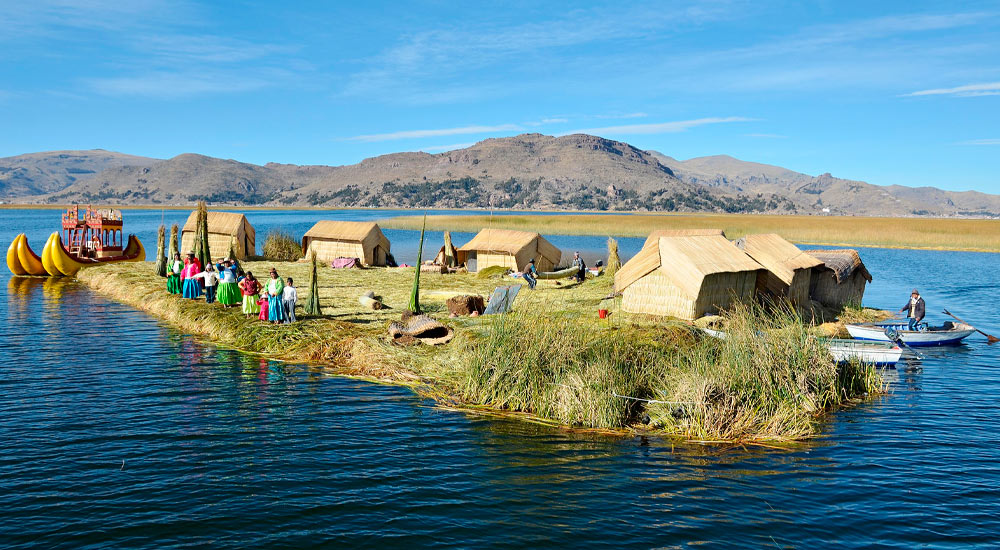

In addition to the mountainous regions, the Incas also practiced innovative agriculture on Lake Titicaca. They constructed artificial islands called “chinampas” using layers of aquatic vegetation and mud. These floating gardens provided a sustainable way to grow crops, and similar methods persist among communities living on the lake’s shores today.
Preserving Traditions and Sustainability
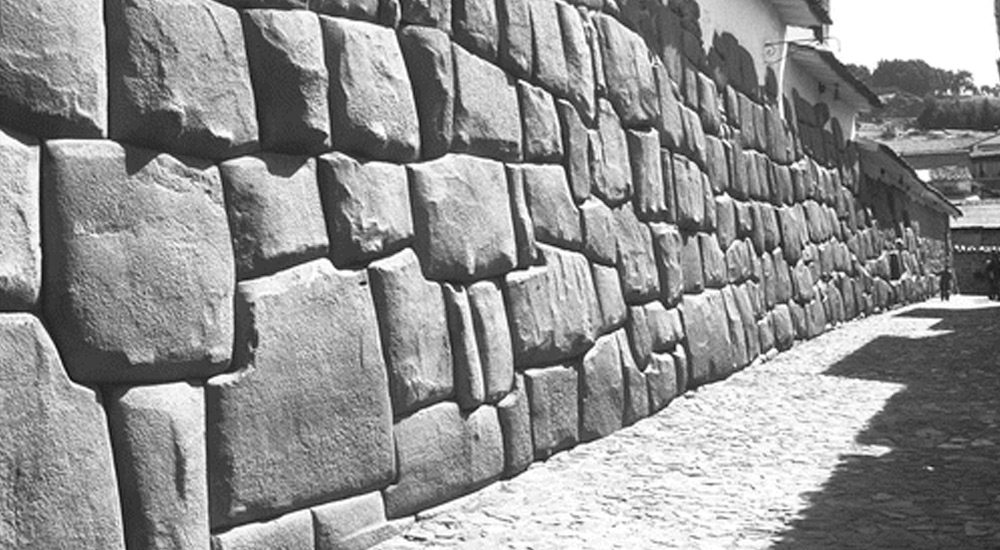

Despite the passage of centuries, the agricultural techniques developed by the Incas remain integral to the survival of Andean communities. Their methods of terracing, crop rotation, and water management have proven to be ecologically sound and sustainable. This approach to farming resonates with modern sustainability practices, making Inca wisdom more relevant than ever.
Challenges and Hopes for the Future
While the Inca agricultural legacy is robust, it faces challenges in the form of climate change, urbanization, and shifts in dietary preferences. Organizations and farmers are working together to preserve these traditions, adapt to changing conditions, and ensure the continuity of Inca-inspired farming practices.
A Timeless Legacy
The story of Inca agricultural tools is a testament to human ingenuity and adaptability. From terraces to qollqas, these tools and practices have transcended time and continue to sustain communities in the challenging environments of the Andes. As we look to the future, the Inca agricultural legacy serves as a source of inspiration and a reminder that solutions to modern challenges can often be found in the wisdom of the past.
The enduring legacy of Inca agricultural tools in modern farming practices is a remarkable testament to the ingenuity of this ancient civilization. The tools and techniques they developed continue to shape agriculture in the Andes, serving as a bridge between the past and the future. As we explore the rich history of Inca agriculture, we gain insights into sustainable farming practices that can benefit us all in an era of environmental consciousness.