Important note: This article is for informational purposes only and does not replace professional medical advice. If you or someone you know is struggling with depression or other mental health issues, please seek the care of a healthcare professional.
Ayahuasca, the Sacred Elixir of the Jungle
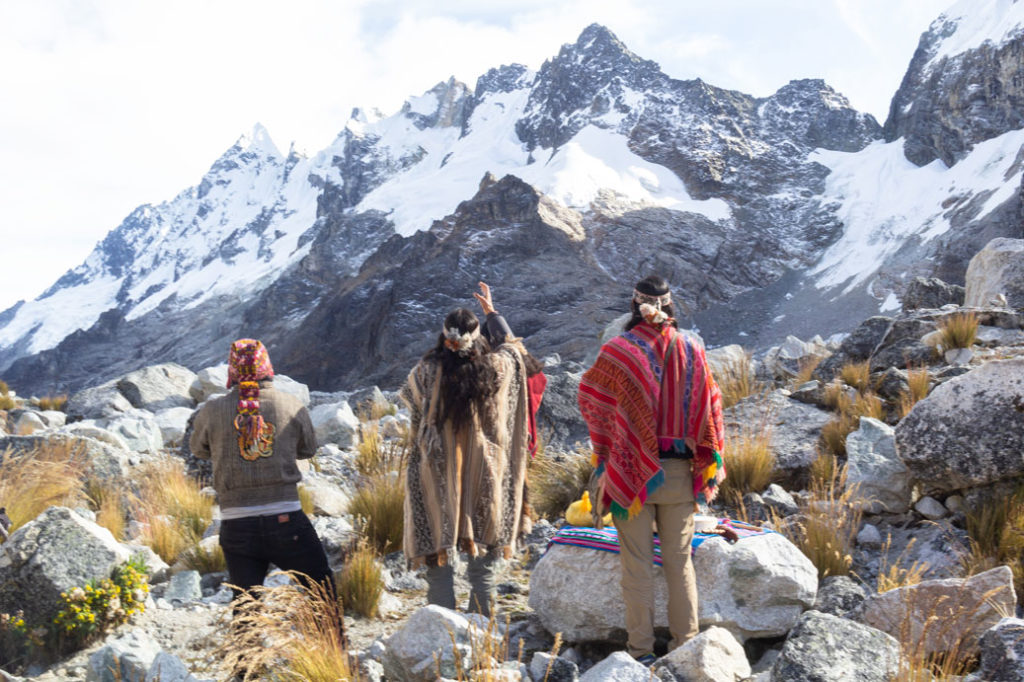
Ayahuasca, known as “yagé” in some regions of South America, is an ancient psychoactive brew used in healing rituals, spirituality, and personal exploration. It is made by combining two plants: the vine Banisteriopsis caapi and the leaves of the chacruna (Psychotria viridis). This Amazonian potion, utilized for centuries by various indigenous cultures, has gained increasing attention worldwide in recent decades, particularly concerning its potential role in the treatment of depression and other mental disorders.
Depression: A Global Mental Health Challenge
Depression is a debilitating mental illness that affects over 264 million people worldwide, according to data from the World Health Organization (WHO). Conventional therapies, including psychotherapy and antidepressant medications, are effective for many individuals. However, not everyone responds well to these treatments, and some experience adverse side effects.
In this context, ayahuasca has drawn the interest of the scientific and mental health community as a potential complementary approach for treating depression and other mood disorders. Although research is in its early stages, initial findings are promising, suggesting that ayahuasca may hold significant benefits for some people.
Ayahuasca and Depression: The Connection
Ayahuasca contains psychoactive substances like dimethyltryptamine (DMT) and harmine, which act on the central nervous system. It is believed that these compounds may positively influence mood, cognition, and perception and offer a different perspective to those who consume it. Some possible mechanisms of action include:
Spiritual Connection: Many individuals who have experienced ayahuasca report profound experiences of spiritual connection. This may help people address feelings of isolation and hopelessness associated with depression.
Emotional Processing: Ayahuasca is said to trigger the release of repressed emotions and help individuals process past traumas and negative emotions, which could be beneficial in the treatment of depression.
Neuroplasticity: It has been suggested that ayahuasca may promote neuroplasticity, the brain’s ability to form new neural connections. This could be relevant to repairing brain circuits affected by depression.
Preliminary Research Findings
Scientific studies on the effects of ayahuasca on depression are limited but promising. Initial results suggest that ayahuasca can offer significant benefits for some people dealing with depression. Some key findings are:
Symptom Reduction: In preliminary studies, a significant reduction in depressive symptoms has been observed after one or several ayahuasca sessions. Participants reported improved mood and increased well-being.
Long-lasting Effects: Although more long-term research is needed, some studies have suggested that the benefits of ayahuasca may persist for weeks or even months after treatment.
Enhanced Resilience: An increase in psychological resilience has been reported by those who have experienced ayahuasca, which could help prevent relapses in depression.
Heightened Mindfulness: Ayahuasca often induces states of expanded consciousness and increased mindfulness, which can help individuals address negative thought patterns and rumination associated with depression.
Challenges and Considerations
Despite promising results, ayahuasca is not a miracle solution for depression and presents significant challenges and considerations:
Legality and Safety: The legality of ayahuasca varies by country and region. Additionally, its consumption carries health risks, such as interactions with other medications and unwanted side effects. Seeking the guidance of healthcare professionals and experienced therapists is essential if considering the use of ayahuasca as part of depression treatment.
Individuality of Experience: The response to ayahuasca is highly individual and can vary significantly from person to person. Not everyone experiences benefits, and some individuals may be overwhelmed by psychedelic experiences.
Ongoing Research: Research on ayahuasca and depression is ongoing, and more scientific evidence is needed to fully understand its effectiveness, safety, and clinical applications.
Ayahuasca, an ancient potion from the Amazon rainforest, has garnered the attention of the scientific community regarding its potential to treat depression. While initial results are promising, more research is needed to fully comprehend its effectiveness and safety.
For those seeking ayahuasca as part of their depression treatment, it is crucial to do so safely and legally under the guidance of healthcare professionals and experienced therapists. Each individual is unique, and what works for one person may not work for another. Ayahuasca is not a miracle solution, but it may offer a new spiritual and emotional perspective in the battle against depression. The key lies in approaching this option with an informed and balanced focus, alongside the guidance of mental health professionals.